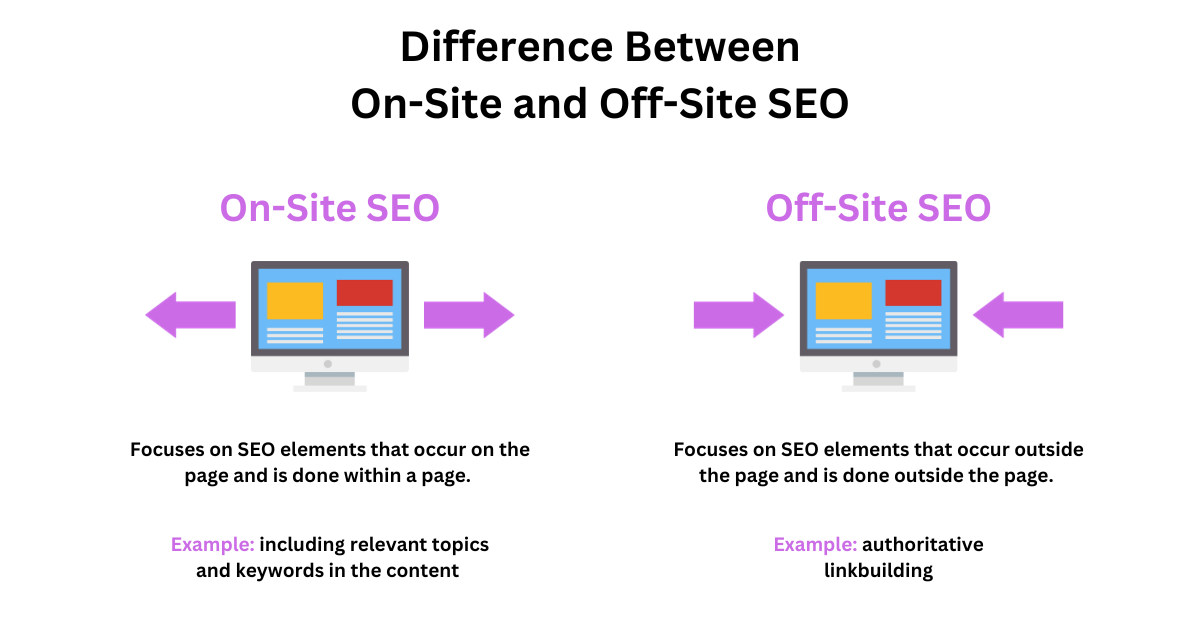
The difference between on-site SEO and off-site SEO is that they target two different sets of SEO factors. The former focuses on elements of SEO that occur on the page, while the latter focuses on factors that occur outside the page.
How do you know which SEO your website needs more? Read on to find out:
- What is On-Site SEO?
- What is Off-Site SEO?
- Why is On-Site and Off-Site SEO important?
- What factors affect On-Site SEO?
- What factors affect Off-Site SEO?
What is On-Site SEO?
On-site SEO (or on-page SEO) is the practice of optimizing websites to rank higher in search engines. This includes optimization of visible content and HTML source code.
An example strategy - finding relevant subtopics
If your page is struggling to rank in the top 10 Google search, one of the reasons could be that it lacks the information that users are looking for. To find out whether this is the case, you'll need to compare the topics of the top-ranking pages with the topics you cover.
You can automate this process using Ahrefs' Content Gap tool. This tool shows you the keywords on which your competitors are ranking and you are not.
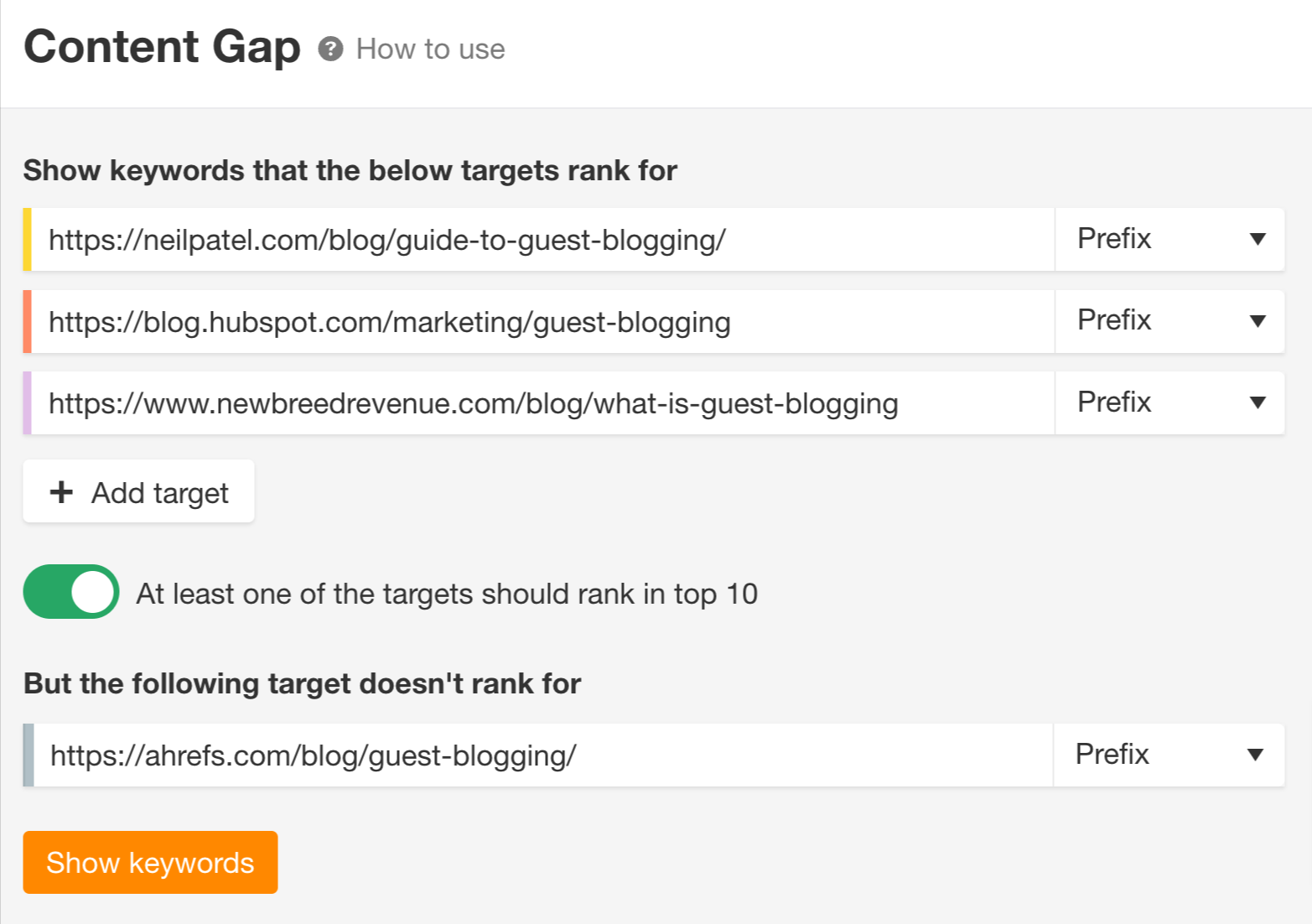 Step 1: Enter the URLs of the pages you want to compare and click "Show keywords".
Step 1: Enter the URLs of the pages you want to compare and click "Show keywords".
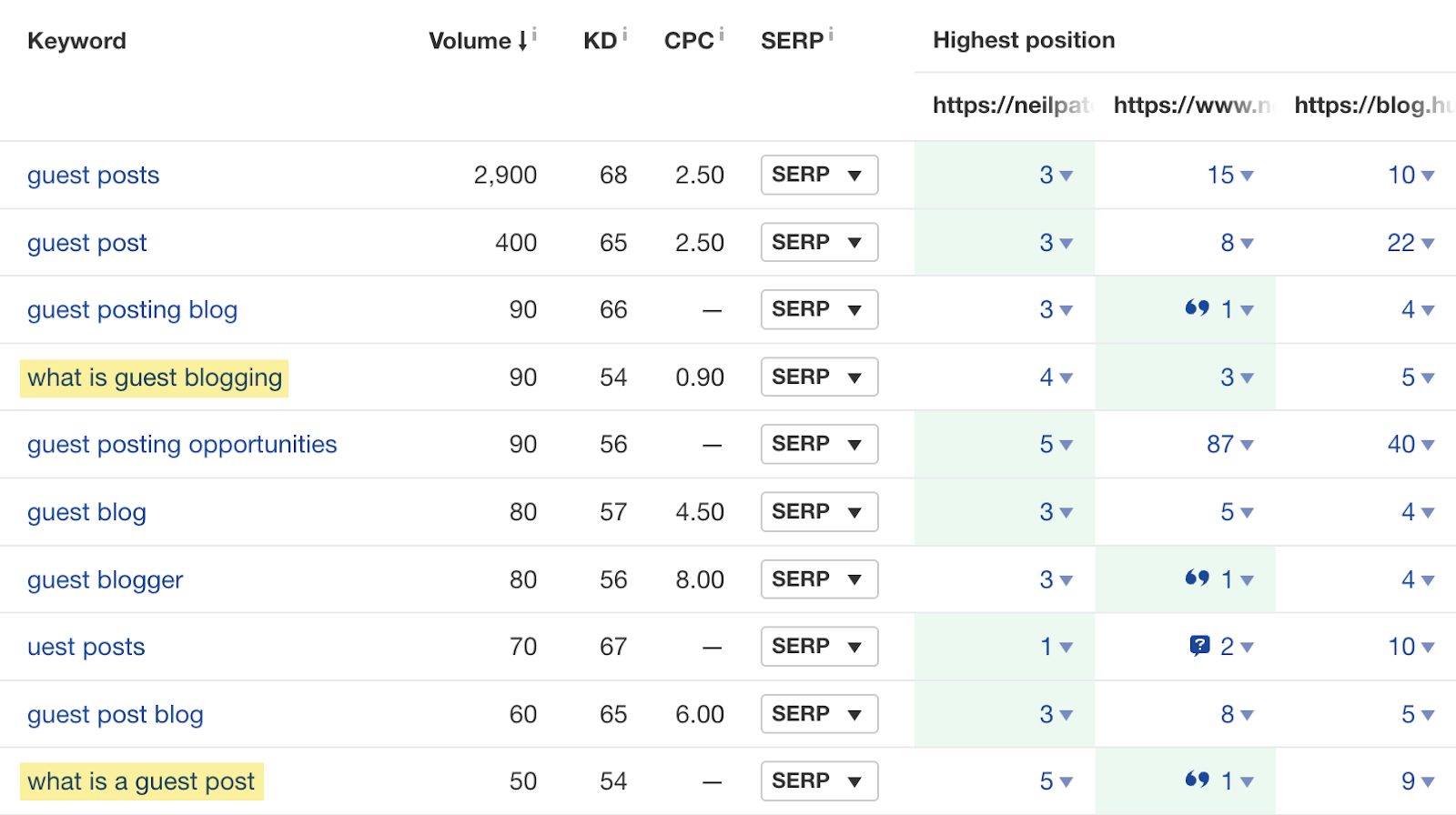 Step 2: Find the topics that are missing from your content. In this example, these might be the definitions of guest blogging and guest posts.
Step 2: Find the topics that are missing from your content. In this example, these might be the definitions of guest blogging and guest posts.
What is Off-Site SEO?
Off-Site SEO embodies any efforts made outside the website to improve its ranking in search engines.
An example strategy - searching for link building opportunities
Backlinks are one of the most important ranking factors (more on this later). You can earn them organically, and you can also "build" them.
There are many link building tactics. One of them is looking for linking patterns among your competitors so that you can get links from the same sites. For this you will need a backlink checker.
Since links from new sites will move the ranking index the most (i.e. sites that don't already link to you), the best way to see linking patterns is to find sites that link to your competitors but not to you. You can do this easily using Ahrefs' Link Intersect tool.
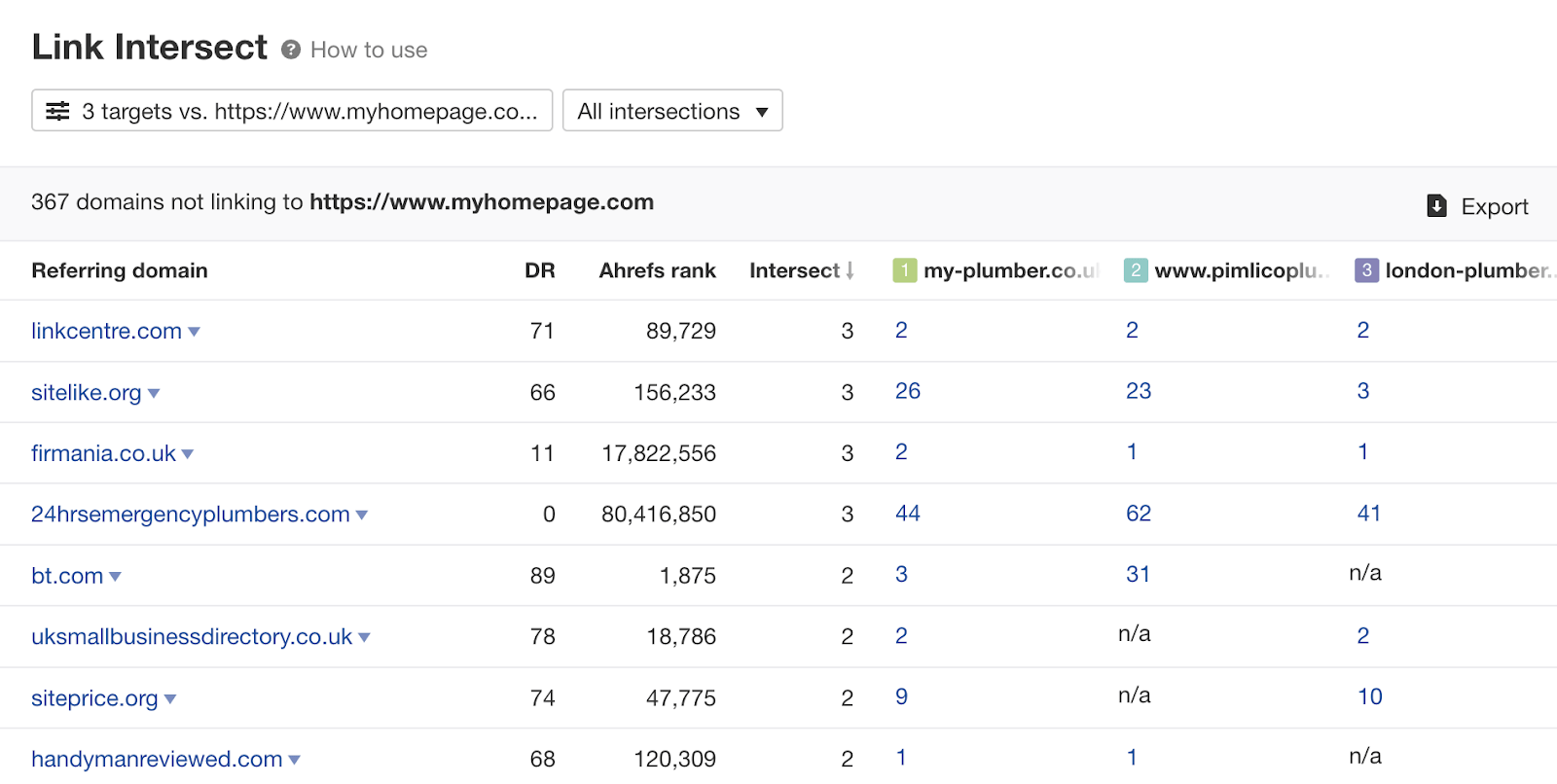 Step 1: Enter the pages you want to compare.
Step 1: Enter the pages you want to compare.
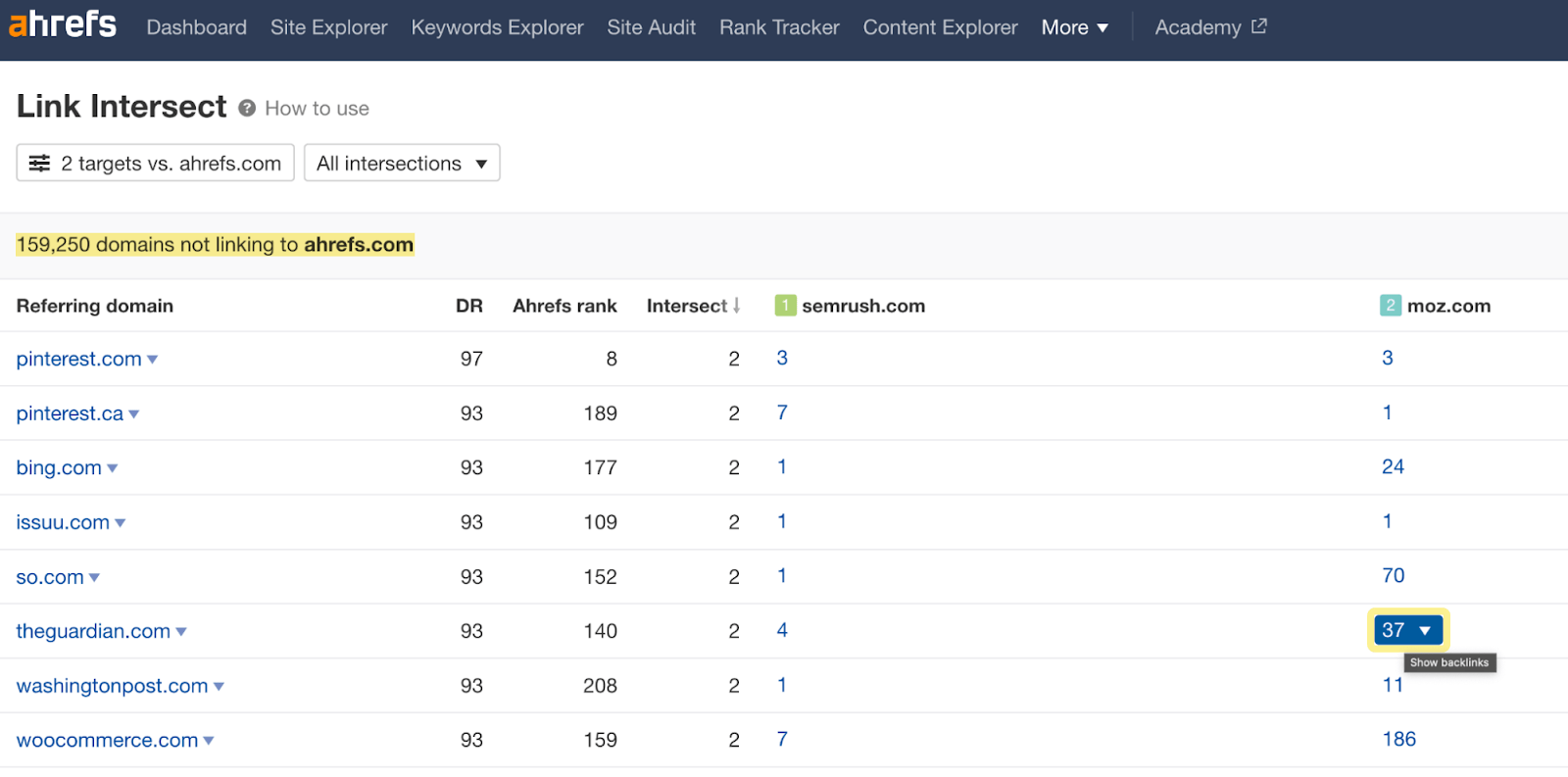 Step 2: Browse the domains in the results. Click on the number of backlinks to your competitors.
Step 2: Browse the domains in the results. Click on the number of backlinks to your competitors.
Why is On-site and Off-site SEO important?
Internal SEO (on-site) and external SEO (off-site) are essentially two sides of the same coin. SEO is most effective when used with both, as Google uses ranking factors that occur both on and off your pages.
Depending on your needs, you can sometimes focus more on one of these types of SEO. However, you probably shouldn't focus on just one of them all the time.
What factors influence On-Site SEO?
In this section, we'll look at some of the most important things you need to consider in order to rank higher on SERPs (search engine results pages) and attract more clicks for your content.
Note: We will talk about known ranking factors and factors that can increase your SERP visibility and consequently attract more website visitors.
Search intent
The purpose of the search indicates the reason for the search. It is one of the strongest ranking factors.
Using search intent in SEO is about understanding what searchers want to get when they write a search query and then providing that information.
Search intent is arguably the most important factor in internal SEO. After all, providing searchers with relevant and useful information is what search engines need to do every second.
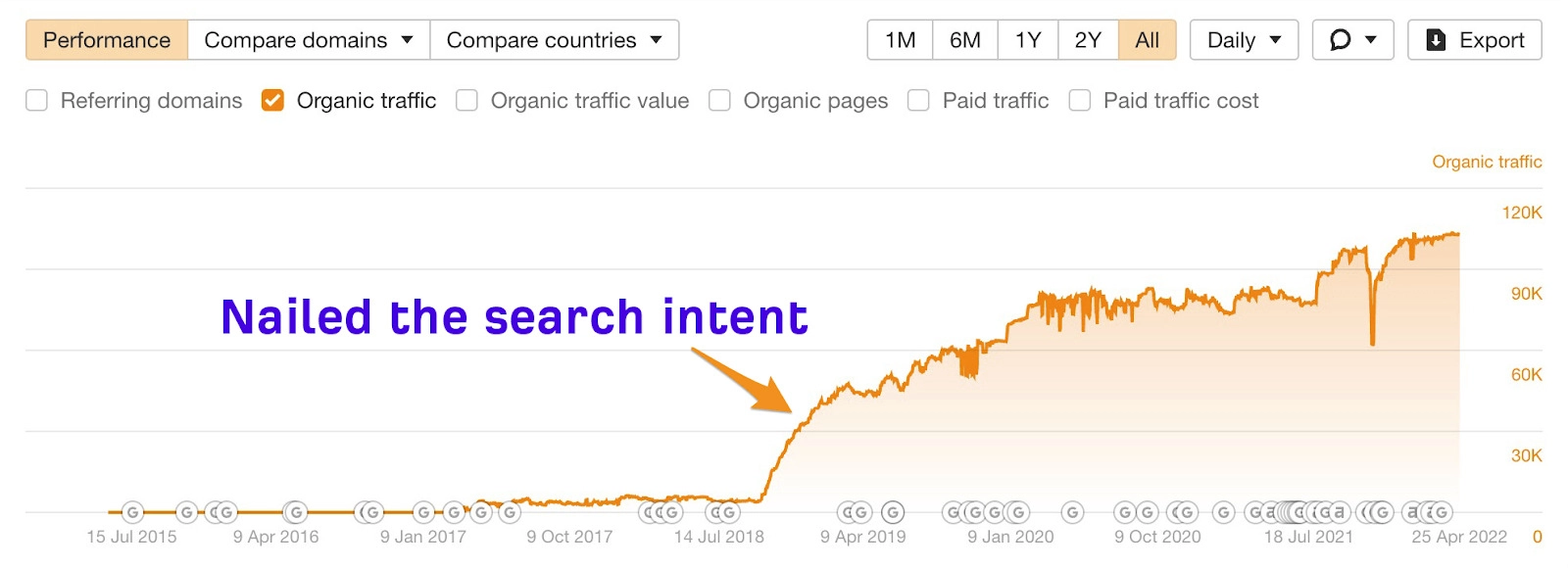 Organic traffic to one page before and after the matching search intent.
Organic traffic to one page before and after the matching search intent.
Optimizing content for search intent involves reviewing the search result pages for a given query and identifying the three 'C's of the search intent:
- Content type - what type of content dominates? Is it a blog post, a product page, a video or something else?
- Content format - some common formats include guides, list posts, reviews, comparisons, etc.
- Content angle - the unique selling point of a piece of content, e.g. 'best', 'cheapest' and 'beginner'.
Once you've identified the three C's of your search intent, you should have a pretty good idea of what type of content Google "recommends" to its users for specific search queries.
Content quality
The intent of the search is very important, but it is not enough to create useful and engaging content. You also need to take care of the quality of your content. Here's what Google has to say about what it looks for in content:
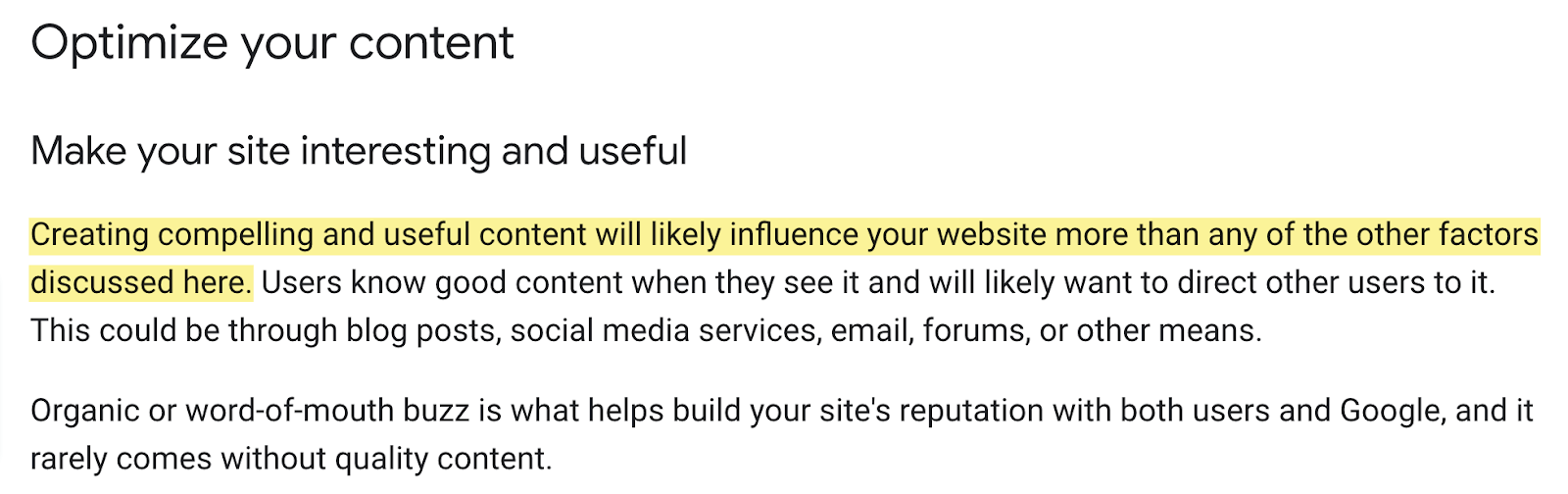
It seems that Google is trying to embed in its algorithms the same attributes that readers value in any piece of content. And, according to Google, that is content:
- Easy to read.
- Clearly organized.
- Fresh.
- Unique.
- Aligned with the E-A-T guidelines.
- Focused on providing essential information to solve the seeker's problem.
But in practice, you also have to create better content than your competitors. This video explains how to increase your chances of achieving this:
URL address
The URL is a minor ranking factor. They have so little weight in ranking websites that Google's John Mueller said they are overrated in SEO and that people should not worry about them.
However, Google's SEO guidelines list URLs as things you should optimize. But you should do it for the user and not for Google.
This is because the user can see the URL both in the address bar and in the SERPs. Based on this information, users can: a) choose to click on some results and not others; and b) know where they are on the site.
So basically this is what an unfriendly URL looks like:
http://example.com/folder1/dir1/dir2/dir3/dir422447478/x2/14032015.htmlAs you can see, the example site does not use HTTPS, and the URL structure is overly complicated and does not really indicate what the page is about:
And here is a handy alternative to it:
https://example.com/seo/ranking-factors.htmlPage titles
Page titles are another small ranking factor. Google uses them to understand what your page is about so that it better matches the intent of a particular search query.
 Excerpt from a Google SERP titled "Keyword Difficulty: How to Estimate Your Chances to Rank"
Excerpt from a Google SERP titled "Keyword Difficulty: How to Estimate Your Chances to Rank"
This title is catchy and descriptive at the same time. Wouldn't you agree?
Naturally, search engines use page titles for similar reasons: to understand what to expect from a page. So, to "satisfy" both parties, you may want to consider the following best practices:
- Make the title eye-catching and precise - write a line that sparks users' interest and accurately describes the uniqueness of your offer.
- Include a targeted keyword in the title - but remember to make it sound natural.
- Keep it to 60 characters - otherwise the description may be cut short, increasing the chances of not showing the relevant information on the SERP.
Meta description
Meta descriptions are not a ranking factor. However, they do appear in the SERPs (directly below the page title) and can therefore influence the click-through rate (CTR).
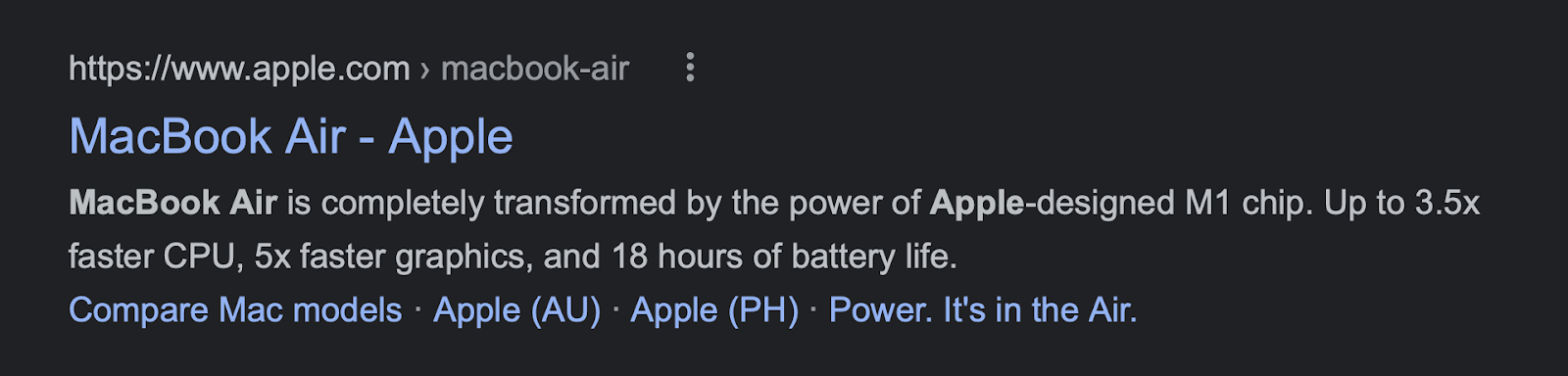 Probably the most logical choice of meta description for such a recognizable product. Apple is only highlighting what has changed in the latest generation product. Not what the MacBook Air is.
Probably the most logical choice of meta description for such a recognizable product. Apple is only highlighting what has changed in the latest generation product. Not what the MacBook Air is.
So the way to optimize meta descriptions is to focus only on the searcher. Here are some important, good SEO practices:
- The description must be appealing enough to attract the user to click, if it's not clickbait (your reputation matters);
- Don't make the description longer than 920 px (try SERPSim);
- The description must match the page title (and vice versa);
- Use a unique description for each page.
Outbound links
An outbound link is a link that points from your page to a page that does not exist on your website.
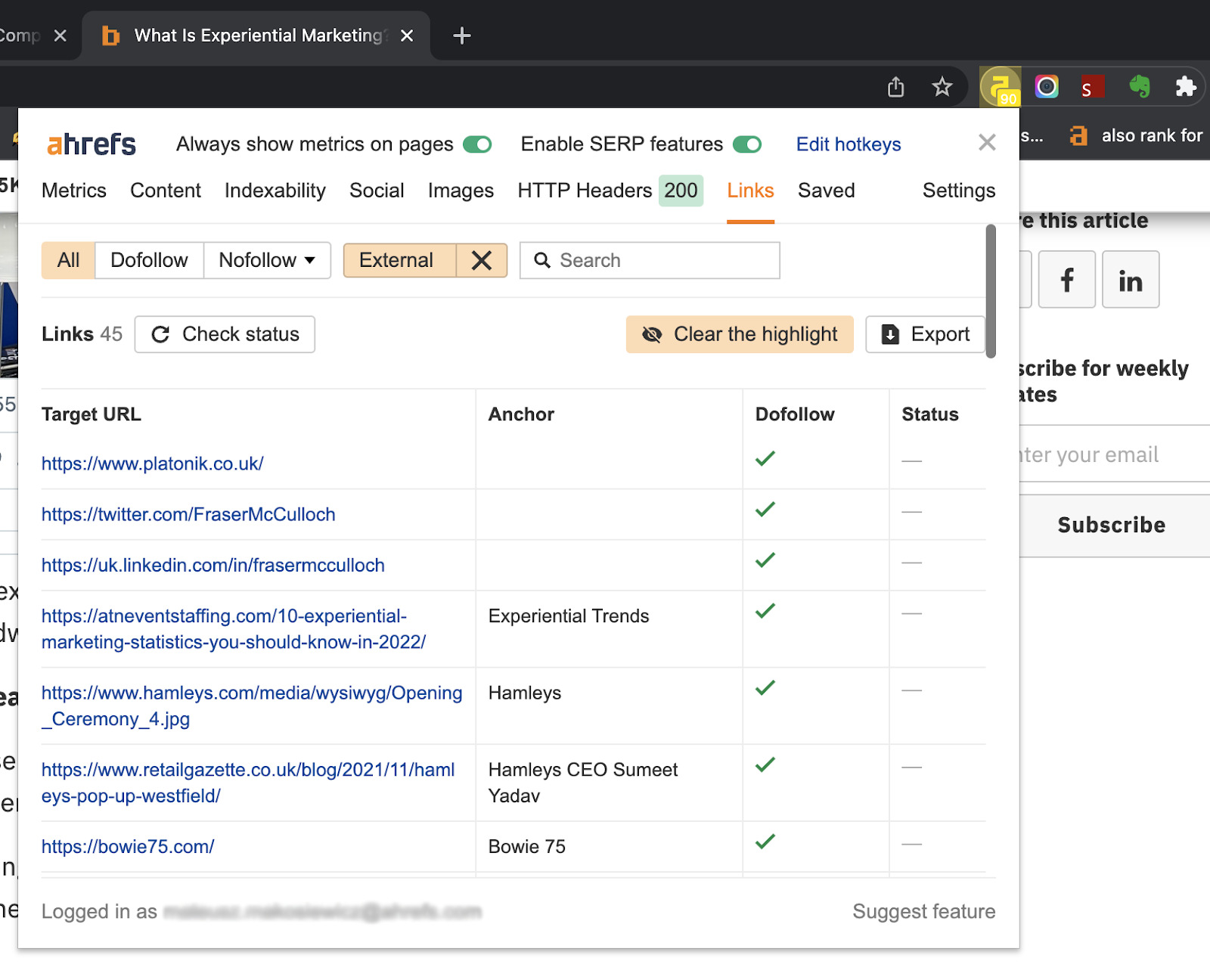 You can view outbound links on any page using the Ahrefs SEO Toolbar.
You can view outbound links on any page using the Ahrefs SEO Toolbar.
External links are unlikely to be a ranking signal. This means that you probably shouldn't try to include external links in your content in the hope of ranking higher.
Instead, you may want to use external links to indicate your sources. This will help establish the legitimacy, transparency and accuracy of your content. In other words, by citing your sources, you will be complying with the E-A-T Search Quality Guidelines.
Schema markup
Schema markup is a code that helps search engines understand your content and display it better in search results.
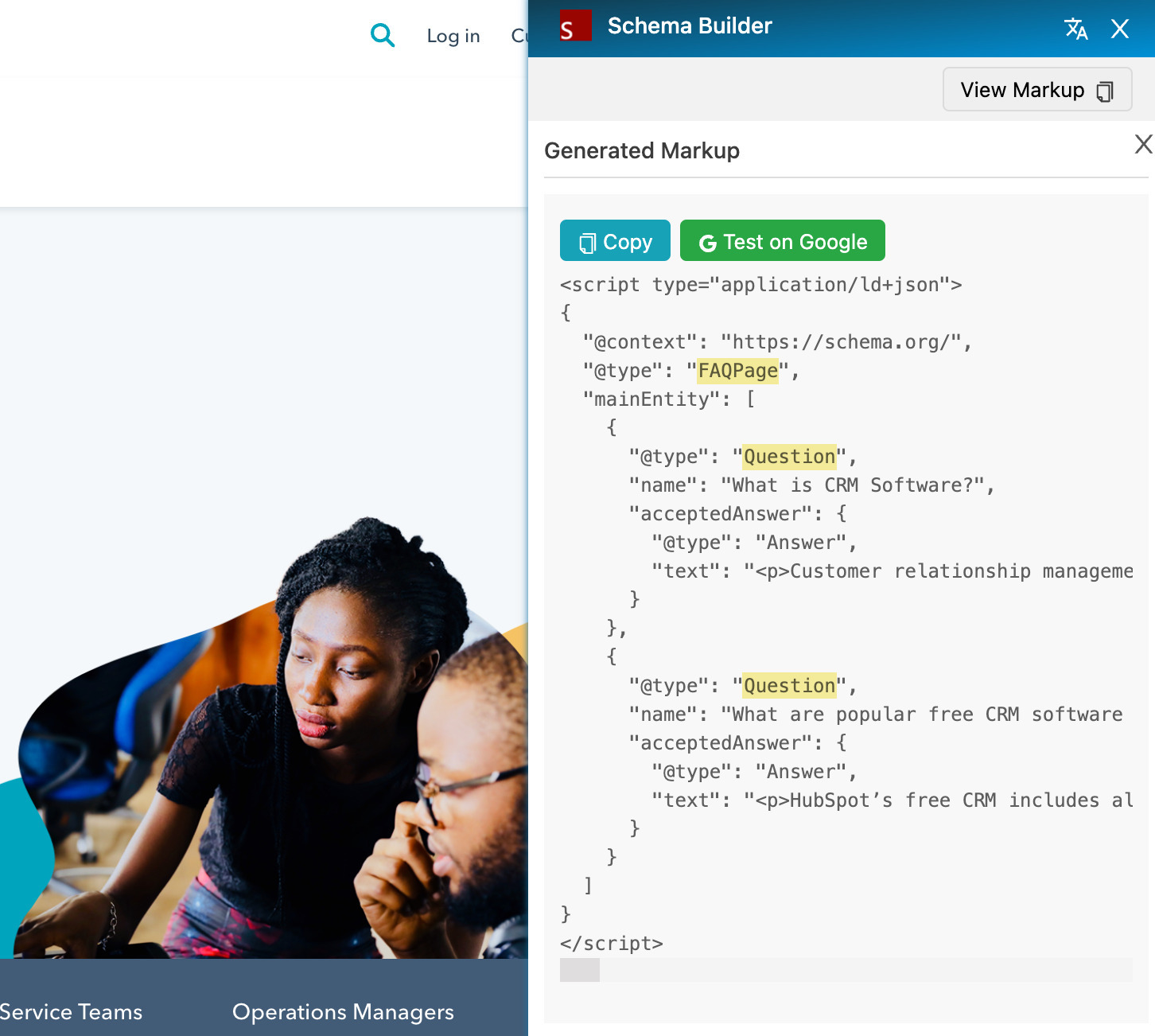
HubSpot uses schema markup to display FAQs in SERP results.
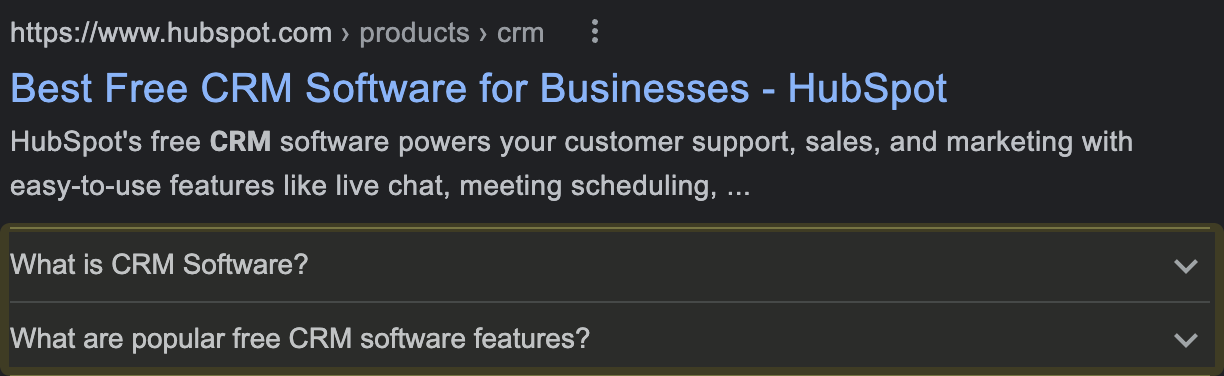
Schema markup is not a ranking factor, but applying it can make your content stand out in SERP results.
Schema markup looks like programming, but it is far from it. Adding schema markup to a page is similar to adding meta tags. To do this, you can use the Schema Builder tool plugin.
Internal links
An internal link is a link from another page on the same website.
Internal links are a ranking factor. Google uses internal links in several ways:
- To discover new pages - internal links provide a crawlable path to the target pages.
- To pass link rankings between pages - internal linking can boost the rankings of other pages you own.
- To make it easier to understand what a page is about- understanding the content of pages helps Google rank them. That's why anchor text is important.
Let's not forget that internal links help users discover content and navigate your website.
For all of the above reasons, you shouldn't neglect internal linking. Ideally, you should add internal links when you create new content or even strategically plan them through content hubs. And remember, it is never too late to add internal links to existing content.
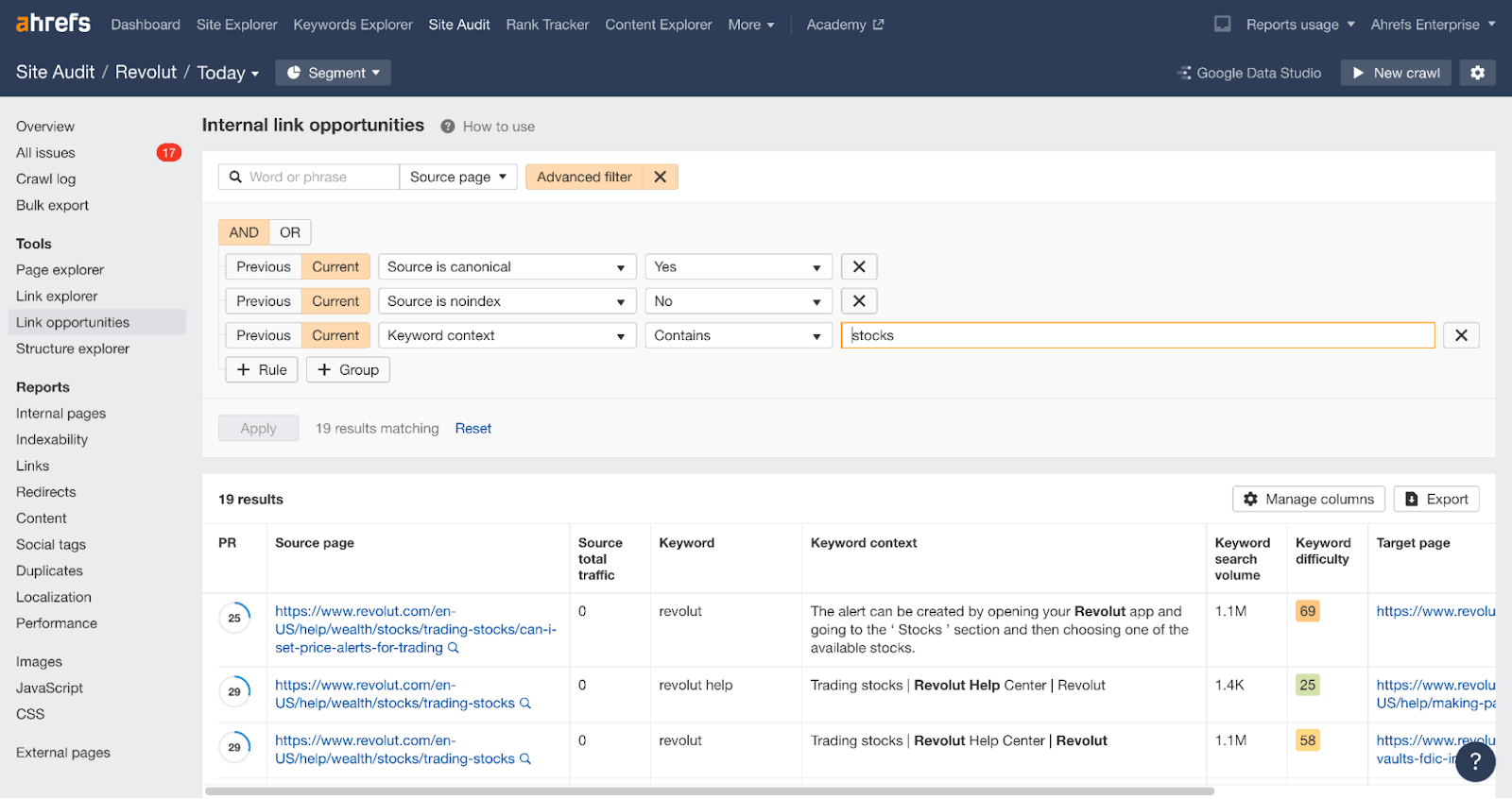
You can checkthe potential internal links on your website for free using Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
Website UX
The user experience (UX) of a website can mean different things to different people. For UX designers, it means the overall impression of a website. But for SEO, the UX of a page or website means its usability. Basically, it means keeping the user interface neat, distraction-free and easy to use.
As a general rule, UX improvements should be applied to the whole website, not just to separate pages. However, if you want to maintain pages with a unique layout, remember that different design means different experience.
So here's what to look out for:
- Avoid intrusive pop-ups - registration forms, exit forms, etc. Do the same with any banner ads that change the layout (see Google's landing page guidelines.
- Make sure important pages are not slow and dull - you should optimize Core Web Vitals.
- Make sure the layout of your website is clear, consistent and usable - try not to overload the user's cognitive capacity.
- Optimize your website for mobile devices - website traffic coming from mobile devices is well over 50%. In addition, Google indexes and ranks content based on mobile versions of websites (mobile-first indexing).
Is page UX a ranking factor? It seems that two factors can affect your rankings here: web KPIs and mobile-friendliness.
When pages have similar content, Google may use page usage signals to rank them, but this will not lead to drastic changes in ranking. Pages that are not optimized for mobile or slow pages may still rank.
What factors affect Off-Site SEO?
As with on-site SEO, we'll talk about factors that are known to have a direct impact on rankings and factors that don't, but can increase visibility and get more natural clicks.
Backlinks
Backlinks are the basis of Google's mathematical formula for page ranking, which assesses the 'value' of a page by taking into account the quantity and quality of other pages that link to that page. Together with search purposes, backlinks are one of the most important ranking factors.
In simple terms, the more backlinks (from unique sites) a page has, the more likely it is to outrank its competitors in SERP results.
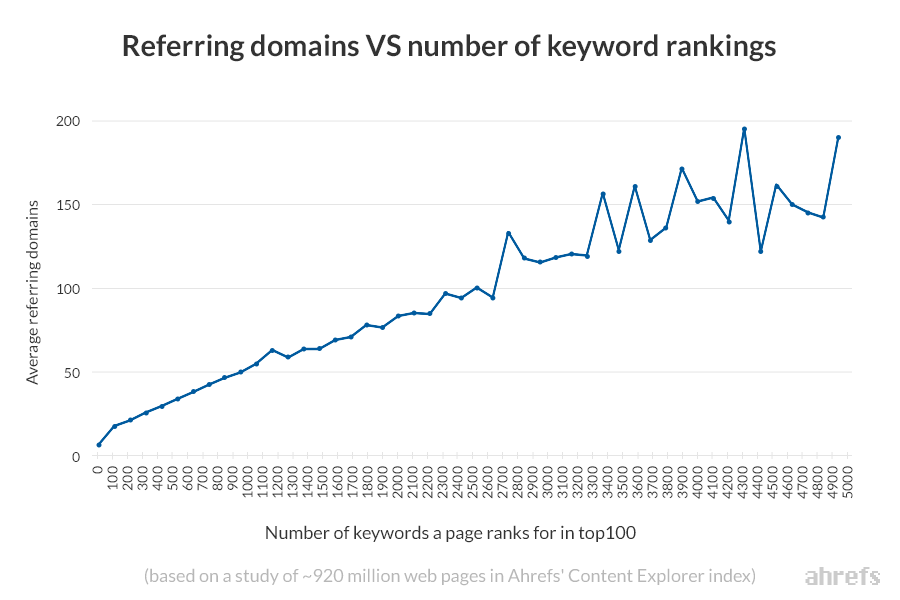
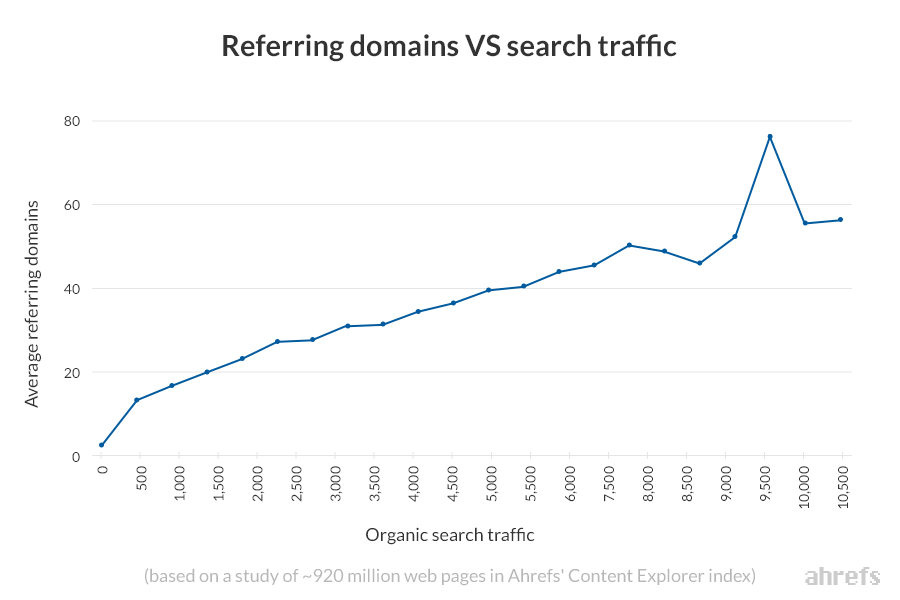
In addition, the more backlinks a page has, the more natural search traffic goes to that page:
However, not all backlinks will affect your ranking equally. You can evaluate a backlink based on these six traits:
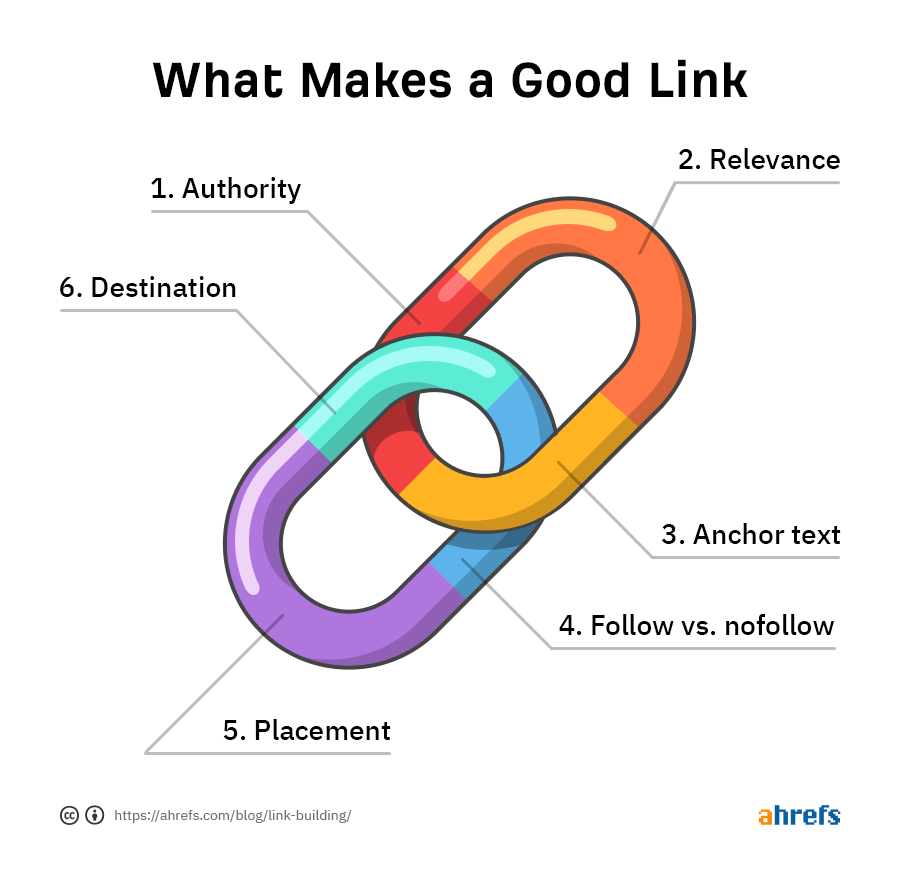
- Authority - if we consider links to be votes, pages with more votes will get stronger votes for other pages.
- Relevance - this is what Google says: "If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.”
- Anchor text - like internal links, backlink text helps Google understand the context of the landing page.
- Follow and nofollow - "Nofollow" is an attribute that tells Google not to consider the link when ranking. The "follow" attribute is its opposite. As a general rule, "followed" links will have a higher impact. By default, all links are "follow" unless otherwise specified.
- Placement - Links that have a higher likelihood of being clicked (e.g. links in the table of contents, links higher up the page) are likely to have more authority.
- Target destination - links can increase the ranking of the specific page to which they point. However, you can transfer some of the link equity to other pages by using internal links.
NAP citations
NAP citations are online mentions of your business that show your company name, address and phone number.
 Example of Trader Joe's NAP citations
Example of Trader Joe's NAP citations
NAP citations are probably a ranking factor that takes into account localized natural search results (learn more here and here). But they may not carry much weight:
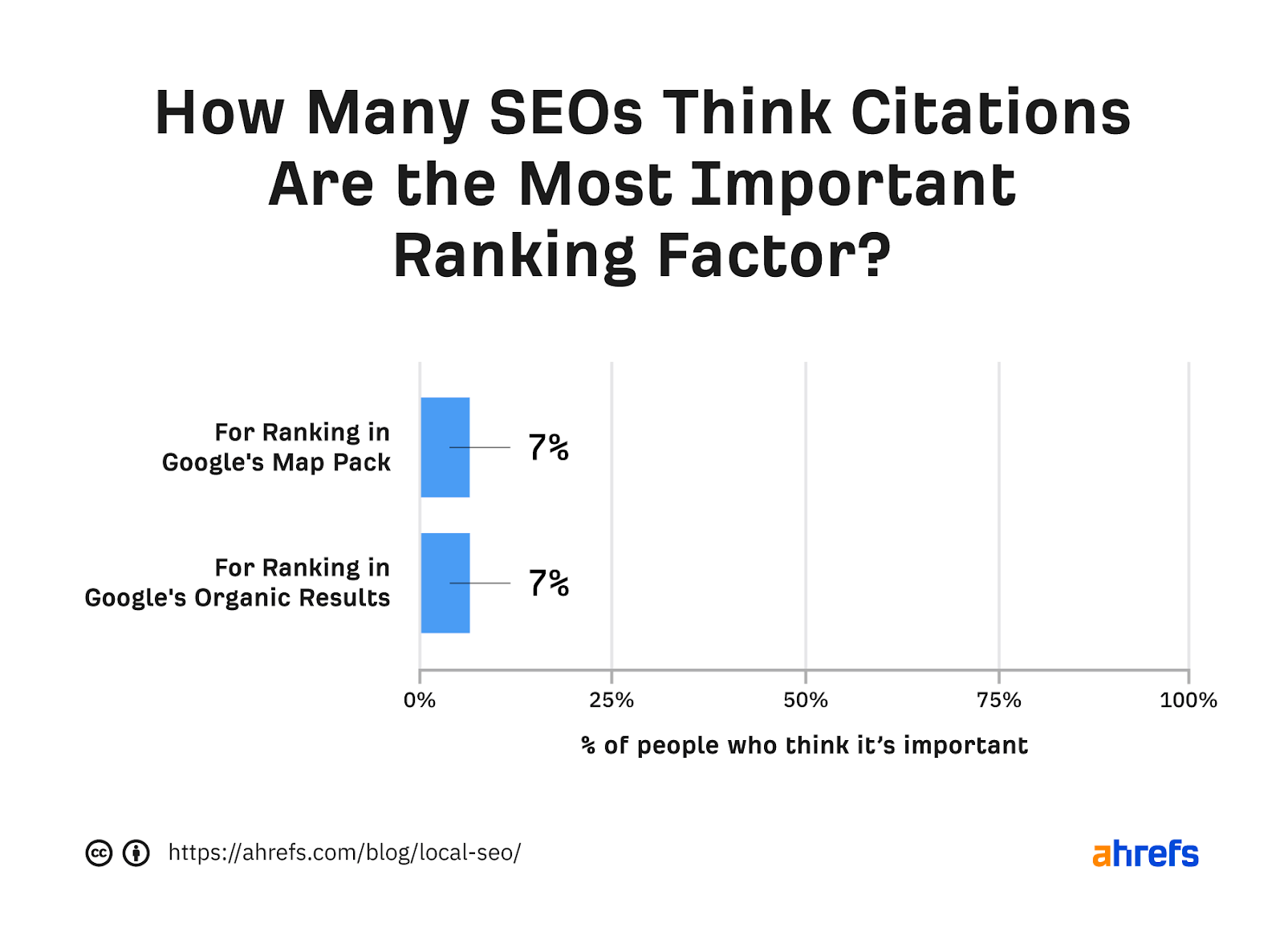
In addition to helping you rank in SERP results, NAP citations are sure to help users find your local business. So here's a short list of best practices you can follow:
- Join big databases like Foursquare. This is where many local data providers get their data.
- Submit your information to the pages of the bigger players - Apple Maps, Yelp, Bing Places, Facebook, etc.
- Submit to other popular directories in your area and field
- Keep citations consistent - you should also match them to guidelines (e.g. Google).
Google Business Profile
Whether Google Business Profile (GBP) is a ranking factor is not even a relevant question here. GBP is simply a requirement to get into the Google Maps suite.
The map pack shows GBPs that are close to the area related to your search query (or based on your location). The search results below the map pack are called local organic results.
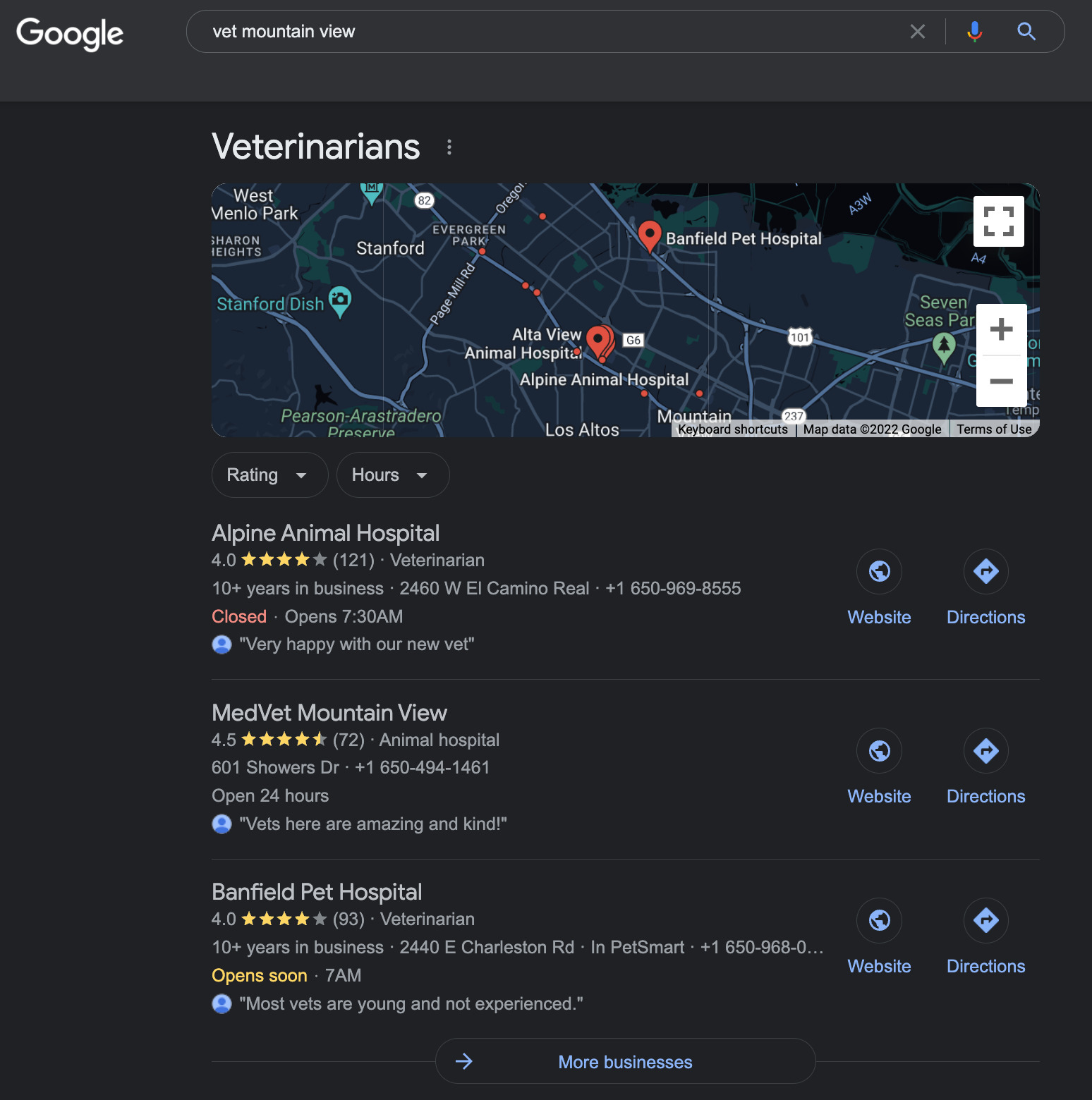 Map pack showing Mountain View Vets GBP.
Map pack showing Mountain View Vets GBP.
Does GBP affect the rankings of the results below the map pack? Most SEO experts say no.
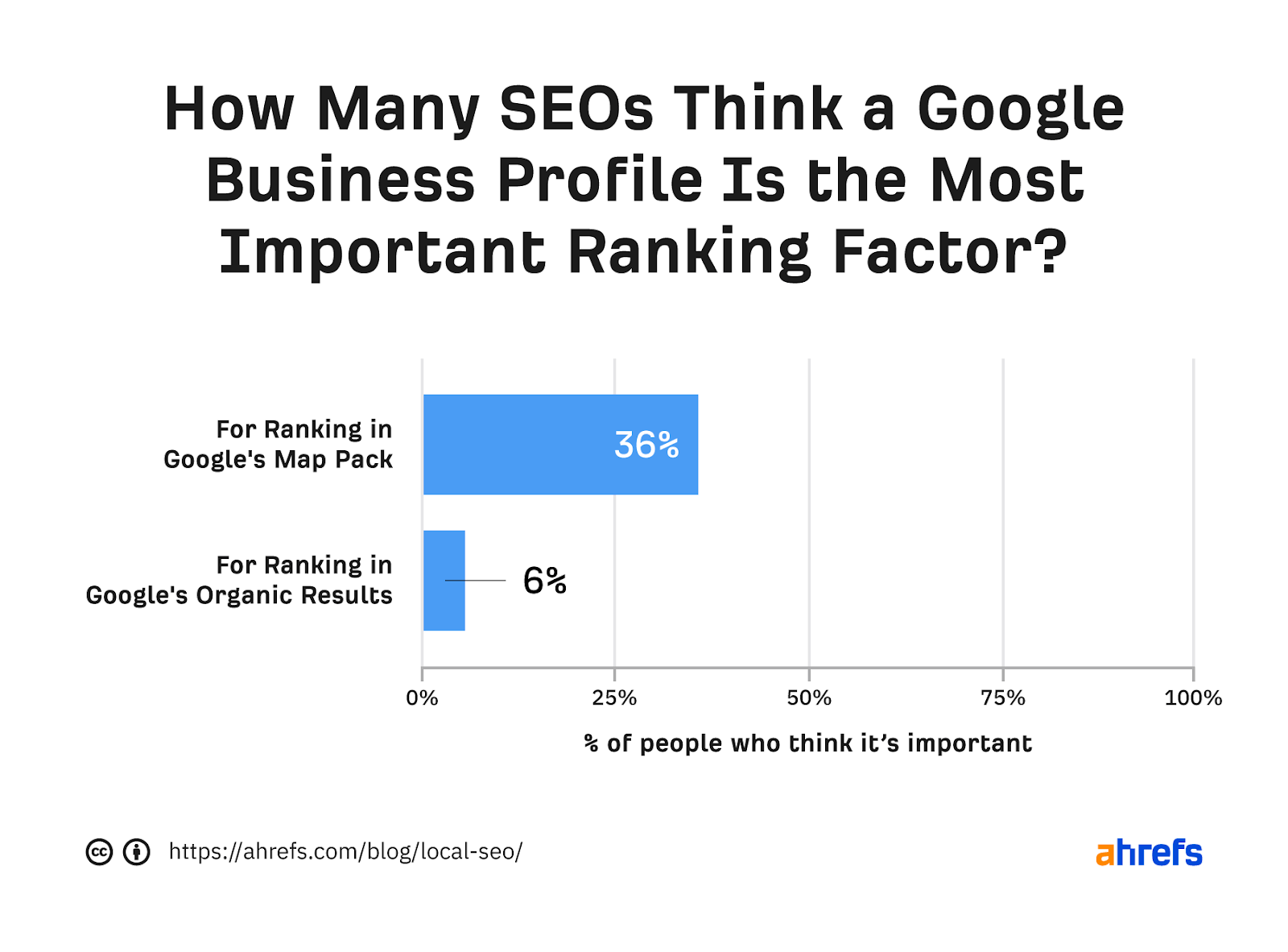
But in general, if your business operates locally, you will definitely want to get GBP. It allows Google to show your business in the map pack and makes it easier for customers to find and contact you.
In addition, GBP helps to get feedback from customers who are near our listing.
Reviews (and ratings)
Let's look at another factor influencing the map pack - customer feedback.
Perhaps the most accurate way to explain this is: customer feedback is a ranking factor that influences the order of results in the map pack, but it is probably of little relevance to the local organic results.
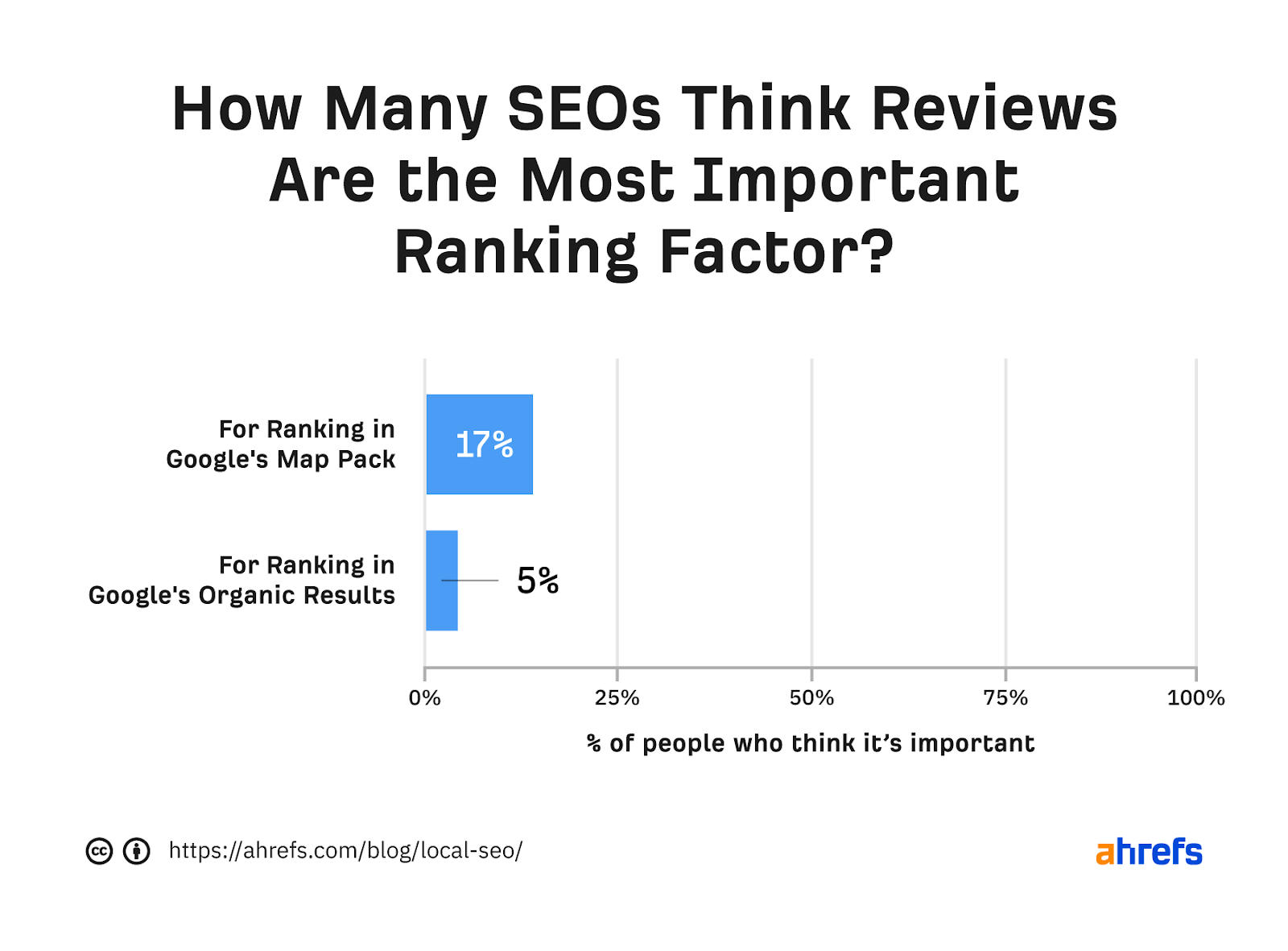
Does Google take into account every single customer review about a business? It is difficult to say. Here it is best to pay particular attention to reviews on GBP and trusted third party sites (G2, Capterra, Yelp, etc.).
As in life, positive feedback will have a positive effect and negative feedback will have a negative effect on your rating.
Let's not forget that rankings and ratings are clearly visible in SERP results and will certainly leave an impression on searchers.
*SIDE NOTES. You can add a rating notation to your schema so that Google can (or can't - it depends on the search engine) display it in natural search results.
Last thoughts
On-Site and Off-Site SEO already seems like a large set of factors and practices, but it's not the whole SEO "landscape". You will probably come across other types or sub-disciplines of SEO such as technical SEO, local SEO, multilingual SEO, etc.
Original text by Mateusz Makosiewicz on Ahrefs: On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO: Different but Equally Important



